Integrate short-term memory
Short-term memory enables your conversational agent to maintain context and coherence by storing structured conversation data during a session. This includes not only message content and roles, but also turn tracking, interruption handling, timestamps, and source metadata.
Built on the OpenAI Chat Completions format with conversational AI extensions, short-term memory integrates seamlessly with large language models while providing flexibility for custom implementations, long-term storage, and dynamic memory updates.
This guide shows you how to access, use, and implement short-term memory in your applications.
This guide applies to Conversational AI Engine version 1.4 and above.
Understand the tech
Conversational AI Engine stores short-term memory in JSON format, following the OpenAI Chat Completions structure. The following example shows the data structure:
Each message contains both standard OpenAI fields and enhanced fields that provide additional context for conversational AI scenarios:
-
OpenAI standard fields:
-
role: Specifies the message sender's role in the conversation. Onlyuserandassistant(agent) are supported in short-term memory.systemmessages are not included. -
content: The specific text content. Currently, short-term memory does not consider multimodal input.
-
-
Conversational AI Engine extensions:
-
turn_id: Dialogue turn identifier. Starts from0and increments with each dialogue turn between the user and agent. -
timestamp: The timestamp of the corresponding message, with millisecond accuracy. -
metadata: Metadata of the message containing the following fields:-
source: Indicates how the message was generated:Value Description user
messageassistant
messageasrSpeech recognition result ✓ ✗ messageText message ✓ ✗ commandMessages generated by RESTful API call ✓ ✓ llmLarge Language Model ✗ ✓ greetingGreeting message ✗ ✓ llm_failureLLM call failed ✗ ✓ silenceSilent reminder message ✗ ✓ -
interrupted: Whether thisassistantmessage was interrupted by human voice:true: This message was interrupted.false(default): This message was not interrupted. The field is hidden whenfalse.
-
interrupt_timestamp: The timestamp when the agent message was interrupted, with millisecond precision. Only exists wheninterruptedistrue. -
original: The complete content actually generated by the LLM. Only exists wheninterruptedistrue.
-
-
Access short-term memory
Conversational AI Engine provides the following methods to access short-term memory:
-
During agent runtime: Call the Retrieve agent history API to retrieve the agent's complete short-term memory in JSON format. This API returns all short-term memory stored during the agent's lifecycle.
-
After agent stops: Agora sends short-term memory to your business server through the message notification service. For details, see Notification event types.
Pass memory content to the LLM
Depending on the llm.vendor field you specify when creating the agent, Conversational AI Engine uses different strategies to pass memory content to the LLM.
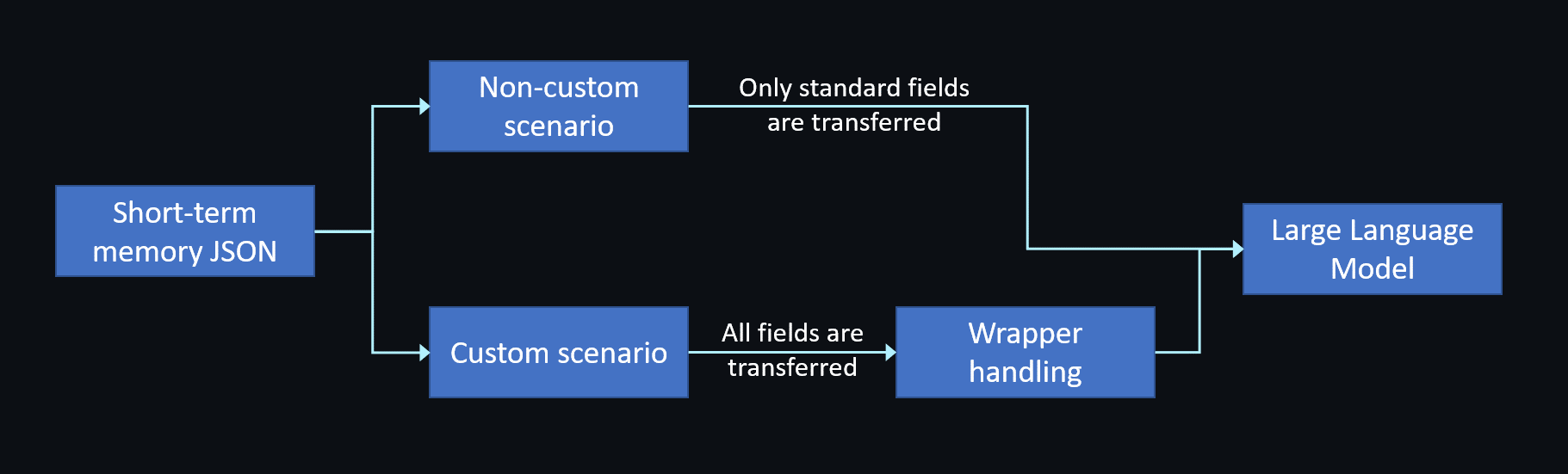
Non-custom scenario
When llm.vendor is not "custom", the engine only transfers the OpenAI standard fields (role and content) from short-term memory to ensure compatibility.
Custom scenario
When llm.vendor is set to "custom", the engine transmits all fields in short-term memory to the LLM. You can implement a wrapper to filter or merge extended fields as needed. For implementation details, see Custom LLM.
Example use cases:
- Add timestamps: Include message timestamps in the
contentfield - Add user context: Prepend user information to the
contentfield - Handle interruptions: Provide the complete
originalcontent for interrupted messages
Combine these enhancements with system_messages to give your LLM deeper conversational awareness, allowing it to maintain user context and gracefully handle interrupted responses.
Convert to long-term memory
Short-term memory disappears when the agent stops. To preserve this data:
- Store short-term memory: Save the short-term memory to your server after the agent stops.
- Inject into new sessions: When creating a new agent, use
llm.system_messagesto inject either the original memory content or a summarized version.
The following example shows how to inject summarized memory content using the system_messages array:
Update memory at runtime
Starting with version 1.4, you can call the Update agent configuration API to update the agent's llm.system_messages field while the agent is running. This enables you to update the memory content dynamically.